Table of contents
1. Confidence Interval & Prediction Interval
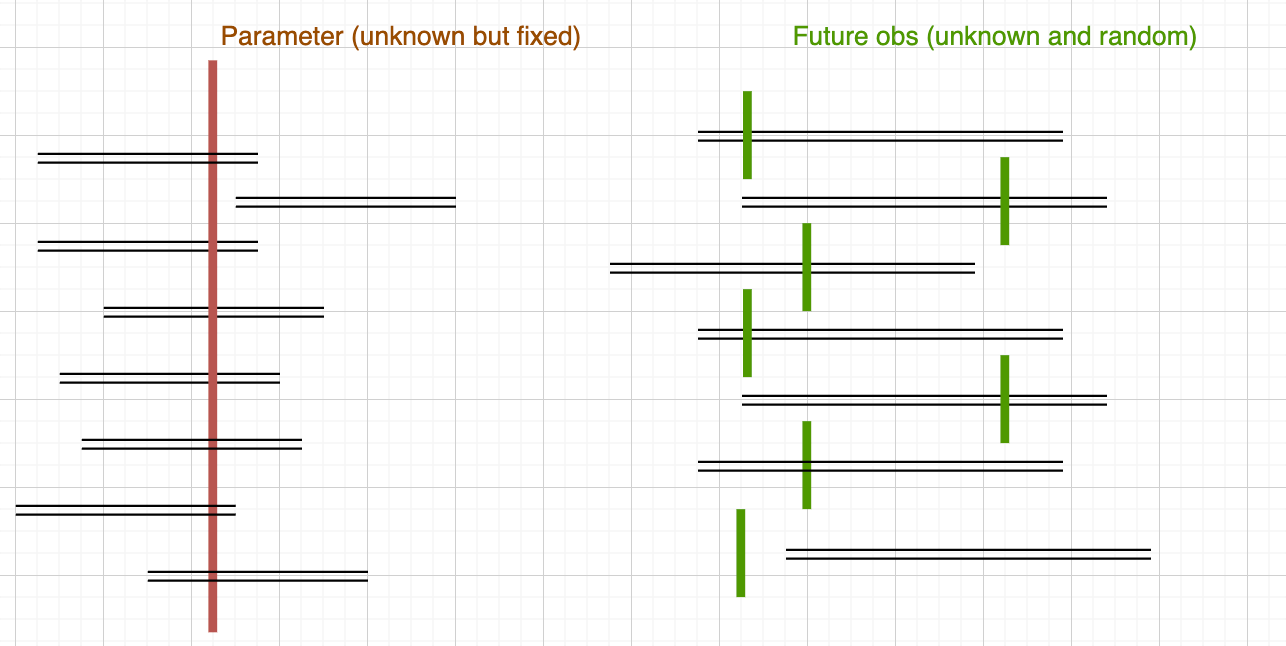
- A confidence interval (CI) is an interval which is expected to typically (like 95%) contain the parameter being estimated. Its counterpart is point estimation.
- A prediction interval (PI) is an interval which is expected to typically (like 95%) contain a future observation, given what has already been observed.
- A parameter is considered unknown but fixed. In contrast, a future observation is usually regarded as random.
- In most cases, a CI is employed to estimate the mean of a random variable, whereas a PI is used to forecast the value of the next sample from that random variable.
- For instance, in linear regression, a CI is constructed for , while a prediction interval is established for . In this context, the PI is typically broader than the CI, assuming the same level of confidence.
2. CI & PI in Meta-Analysis
In the REM case,
CI for ,
We use to construct PI for ,
Hence, PI for ,
We can see that PI for is broader than CI for .