Pan, W., & Peña, J. (2021). A replication and expansion of the exposure effects of online model photos and social comparison goals on planned behaviors and self-efficacy to lose weight. New Media & Society, 146144482110553. https://doi.org/10.1177/14614448211055367
Table of contents
Problem statement
This study focuses on the exposure effects of {models with higher or lower weight which vary in physical attractiveness} and {presence of social comparison instructions} on men and women’s planned behaviors to lose weight (i.e. intentions and attitudes) and self-efficacy to lose weight (i.e. beliefs about one’s capacity and control over losing weight).
Previous viewpoints: studies document that social media use, particularly Instagram use, is associated with body dissatisfaction and self-objectification as it enables individuals to compare themselves to attractive influencers and models (Cohen et al., 2019; Fardouly and Holland, 2018; Tiggemann and Anderberg, 2019).
Significance: Considering that it is still unclear how and why exposure to body positive content may increase or decrease individuals’ body satisfaction, charting the exposure effects of online models’ photos on perceivers’ body image concerns has theoretical and societal importance.
Concept clarification:
- Body satisfaction: defined as satisfaction regarding one’s weight or general self-appearance, as the main outcome variable for exposure effects (see Want, 2009).
- Planned behaviors: include intentions, attitudinal beliefs, and self-efficacy beliefs, which are fundamental factors in the theory of planned behaviors (Ajzen, 1985) that may effectively predict individuals’ future decisions (Ajzen and Kruglanski, 2019).
Method
- The number of subjects: N=418 (218 men & 200 women)
- Model pictures: 48 = 6 ×2(gender)×2(attractiveness)×2(weight)
- Experiment design: 2×2×2 ×2(presence of comparison instructions) = 16 conditions
- Procedure:
- Answer the trait social comparison scale & indicate their gender
- Half of the participants received social comparison instructions (random)
- Each participant were presented with 6 model pictures in a combination
- Rate perceived physical attractiveness & weight status
- Finish manipulation check questions & planned behavior scale & self-efficacy scale
- Demographic information
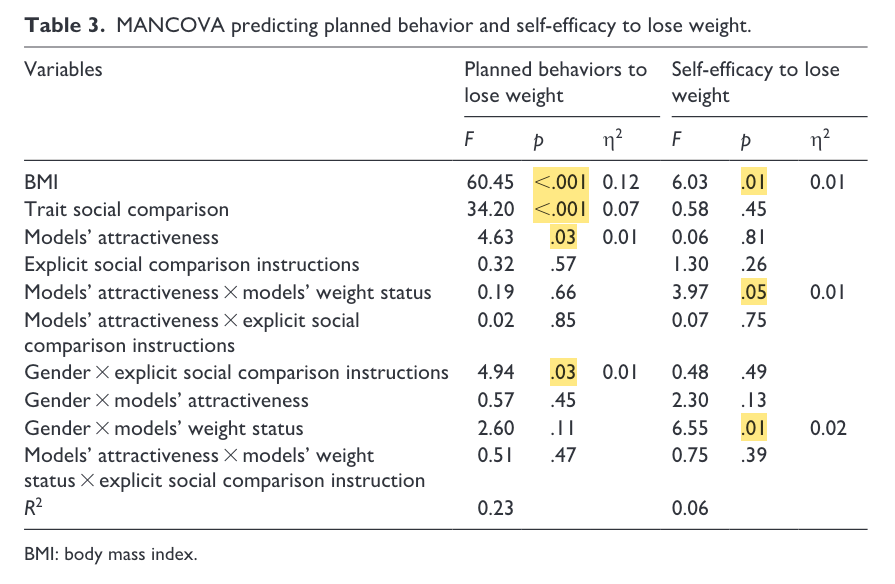
- Data analyses: MANCOVA
- Covarites: 1) BMI; 2) trait social comparison
- DV: 1) planned behavior; 2) self-efficacy
- Factors: 1) model’s attractiveness; 2) model’s weight status; 3) explicit social comparison manipulation; 4) gender
Results
More than two-way ANOVA & Interaction
When interpreting a three-way interaction term in ANOVA, it is important to recognize that this term may indicate the dependence of a two-way interaction on a third variable. Consequently, one should exercise caution in directly interpreting two-way interaction terms without considering the three-way interaction. If the three-way interaction term is statistically significant, the analysis should proceed by partitioning the sample based on one of the factors. Subsequently, a two-way ANOVA can be conducted within each level of this factor. This approach may reveal that the two-way interaction is significant at certain levels of the factor, but not at others. Hence,
- A significant interaction between two factors → the effect of one factor on the dependent variable depends on the level of the other factor.
- A significant three-way interaction → the two-way interaction between any two factors depends on the level of the third factor.
(reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AHRJSY1HpLU)