The Johnson-Neyman Technique is a statistical method used to determine the range of values of a moderator variable for which the relationship between two variables (e.g. DV ~ IV) is statistically significant.
Table of contents
1. Motivation
A moderation model with a moderator M:
Reformulate:
From the equation, we know that when M changes, the relationship between X and Y (i.e. ) changes accordingly. On the one hand, we hope to understand how the relationship between X and Y varies with changes in M, such as when the direction of the relationship begins to reverse. On the other hand, we want to know how the significance of the relationship between X and Y varies with changes in M. This is where the Johnson-Neyman technique comes into play.
2. Example
Reference: Johnson Neyman in R (2 detailed examples) (tidypython.com)
Model: mpg ~ hp × wt (wt is the moderator)
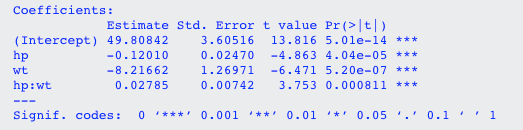
JN will provide the following figure:
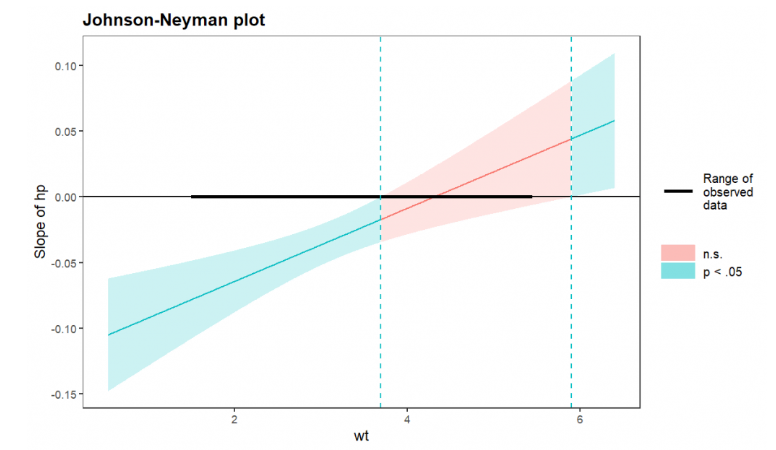
Green area represents a significant relationship between IV and DV: (1) When wt < 3.69,the effect of hp on mpg is significantly negative; (2) When wt > 5.90,the effect of hp on mpg is significantly positive; (3) When 3.69 < wt < 5.90, the effect of hp on mpg is not significant.
3. Software
- SPSS: PROCESS
- R: Package interactions